저번 포스팅에서는 forward와 backward 그리고 활성화 함수인 Relu함수를 클래스로 구현해보았습니다. 이번에는 cross entropy와 softmax도 함께 구현해보도록 하겠습니다.
cross entropy 와 softmax
보통 신경망에서 분류할 때, softmax를 사용하며, softmax는 신경망의 출력층 마지막에서 사용합니다. softmax와 함께 오차 함수로 cross entropy함수를 사용하는데, cross entropy error는 줄여서 CEE라고도 쓸 수 있습니다. 식은 아래와 같습니다.
y_k는 신경망에서 나오는 출력 값이며 0에서 1사이의 값이 나옵니다. t_k는 정답 레이블이며, 정답이 아닌 나머지 t_k가 0이며, log는 밑이 e인 자연로그입니다. cross entropy를 Python으로 작성할 때 아주 작은 값을 더해줘야 하는데, 그 이유는 y가 0인 경우 -inf값을 예방하기 위해서 입니다.
파이썬으로 구현하면 아래와 같이 구현할 수 있습니다.
import numpy as np
def crossEntropyError(y, t):
return -np.sum(t*np.log(y))
그러나 위와 같이 구현하게 된다면, y가 0되버리는 경우에 -inf값이 나올 수 있으므로 아주 작은 값을 더해줘야 합니다.
import numpy as np
def crossEntropyError(y, t):
delta = 1e-7 #아주 작은 값 (y가 0인 경우 -inf 값을 예방)
return -np.sum(t*np.log(y+delta))
그래서 cross entropy를 구현할 때는 위와 같이 아주 작은 값을 y에 더해줘야 합니다.
import numpy as np
def crossEntropyError(y, t):
delta = 1e-7
return -np.sum(t*np.log(y+delta))
t = np.array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]) # label = 5
y = np.array([0.1, 0.03, 0.05, 0.2, 0.9, 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.12, 0.03])
print("-- 정답인 경우 --")
print("CEE :", crossEntropyError(y, t))
y = np.array([0.1, 0.03, 0.05, 0.2, 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.12, 0.03, 0.9])
print("-- 오류인 경우 --")
print("CEE :", crossEntropyError(y, t))
softmax는 아래와 같이 파이썬으로 구현할 수 있습니다.
def softmax(a):
c = np.max(a)
exp_a = np.exp(a)
sum_exp_a = np.sum(exp_a)
y = exp_a / sum_exp_a
return y
Softmax With loss 클래스 만들기
클래스 이름은 원하는 걸로 하셔도 되지만, 저는 명확한 구분을 위해 이렇게 짓겠습니다. 위에서 softmax와 cross entropy 함수 두개 다 구현했기 때문에, 추가 할 함수는 없으며 loss함수에 대해 forward와 backward를 사용하여 클래스만 구현하면 Softmax With loss 클래스를 만들 수 있습니다.
import numpy as np
def cross_entropy_error(y, t):
delta = 1e-7
return -np.sum(t * np.log(y + delta)) / y.shape[0]
def softmax(a):
c = np.max(a) # 추가한 부분
exp_a = np.exp(a)
sum_exp_a = np.sum(exp_a)
y = exp_a / sum_exp_a
return y
class SoftmaxWithloss:
def __init__(self):
self.loss = None
self.y = None
self.t = None
def forward(self, x, t):
self.t = t
self.y = softmax(x)
self.loss = cross_entropy_error(self.y, self.t)
return self.loss
def backward(self, dout=1):
batch_size = self.t.shape[0]
dx = (self.y - self.t) / batch_size
return dx
여기까지 구했다면 아래와 같이 2층짜리 신경망을 쉽게 만들어볼 수 있습니다.
import numpy as np
def cross_entropy_error(y, t):
delta = 1e-7
return -np.sum(t * np.log(y + delta)) / y.shape[0]
def softmax(a):
c = np.max(a)
exp_a = np.exp(a)
sum_exp_a = np.sum(exp_a)
y = exp_a / sum_exp_a
return y
class Affine:
def __init__(self, W, b):
self.W = W
self.b = b
self.x = None
self.dW = None
self.db = None
def forward(self, x):
self.x = x
out = np.dot(x, self.W) + self.b
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = np.dot(dout, self.W.T)
self.dW = np.dot(self.x.T, dout)
self.db = np.sum(dout, axis=0)
return dx, self.dW, self.db
class Relu:
def __init__(self):
self.mask = None
def forward(self, x):
self.mask = (x <= 0) # 설명 : x 값이 0 이하면 True 크면 False; True, False 를 가지는 numpy 배열
out = x.copy()
out[self.mask] = 0 # 설명 : mask 가 Ture 인 곳은 x 의 원소 값이 0, False 인 곳은 그대로 출력
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dout[self.mask] = 0
dx = dout
return dx
class SoftmaxWithloss:
def __init__(self):
self.loss = None
self.y = None
self.t = None
def forward(self, x, t):
self.t = t
self.y = softmax(x)
self.loss = cross_entropy_error(self.y, self.t)
return self.loss
def backward(self, dout=1):
batch_size = self.t.shape[0]
dx = (self.y - self.t) / batch_size
return dx
x = np.array([[1, 2]])
w1 = np.array([[1, 3, 5], [2, 4, 6]])
w2 = np.array([[1, 4], [2, 5], [3, 6]])
b1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b2 = np.array([1, 2])
# 순전파
affine1 = Affine(w1, b1)
affine2 = Affine(w2, b2)
relu1 = Relu()
relu2 = Relu()
# 은닉 1층
out1 = affine1.forward(x)
relu_out1 = relu1.forward(out1)
# 은닉 2층
out2 = affine2.forward(relu_out1)
relu_out2 = relu2.forward(out2)
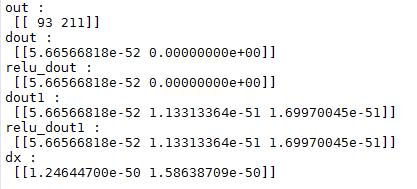
print('out : \n', relu_out2)
# softmax
t = np.array([[0, 1]])
softmaxWithloss = SoftmaxWithloss()
loss = softmaxWithloss.forward(relu_out2, t)
# 역전파
dout = softmaxWithloss.backward()
# dout = relu_out2
print('dout : \n', dout)
# 은닉 2층
# relu 통과
relu_dout = relu2.backward(dout)
print('relu_dout : \n', relu_dout)
# affine 통과
dout1, dw2, db2 = affine2.backward(relu_dout)
print('dout1 : \n', dout1)
# 은닉 1층
relu_dout1 = relu1.backward(dout1)
print('relu_dout1 : \n', relu_dout1)
dx, dw1, db1 = affine1.backward(relu_dout1)
print('dx : \n', dx)