텐서플로우 사용하기, Hello, Tensorflow! (실행 구조와 구구단 출력)
언어를 새로 배우거나 무언가를 새로 배울 때, 우리는 가장 먼저 Hello, world! 를 가장 먼저 찍어냅니다. Tensorflow 을 포스팅 하는 기념으로 Hello, Tensorflow!를 찍어보겠습니다.
Tensorflow 기본 구조
우선 텐서플로우가 설치가 안되어 있다면 아래와 같이 설치 해주세요.
pip install tensorflow
설치가 되었다면 모듈을 가져와서 tf를 호출합니다.
import tensorflow as tf
그리고 그래프를 실행할 세션을 구성합니다. (참고로 포스팅에서 사용하는 tf는 1.x 버전입니다.)
sess=tf.Session() # 그래프를 실행할 세션을 구성한다.
hello=tf.constant('Hello, Tensorflow')
# # # # # # # # 모델을 구성하는 부분 ↑
# # # # # # # # 모델을 실행하는 부분 ↓
print(sess.run(hello))
print(str(sess.run(hello),encoding="utf-8"))
위에서 변수를 정의 햇으나 실행은 정의한 시점에서 실행되는 것이 아니고 Session 객체와 run 메소드를 사용할 때 계산되어 실행됩니다.
이번에는 간단하게 덧셈을 출력해보겠습니다.
import tensorflow as tf
x=tf.constant(35, name='x') # x라는 상수값을 만들어 숫자 35 지정
y=tf.Variable(x+5, name='y') # y라는 변수를 만들고 방정식 x+5로 정의
model=tf.global_variables_initializer() # 변수 초기화
with tf.Session() as sess: # 값을 계산하기 위한 세션 생성 (세션 열기)
sess.run(model) # 위에서 초기화한 model을 실행하겠다.
print(sess.run(y)) # 변수 y를 실행하며 현재값 출력
원래는 세션을 연 뒤에는 닫아야는데 with절 후에는 자동으로 닫히기 때문에 그냥 출력합니다. 또한 텐서플로우는 빌딩 구조와 실행구조(session)가 분리되어 있습니다.
# 빌딩 과정
import tensorflow as tf
x2 = tf.linspace(-1.0, 1.0,10) # -1 ~ 1 사이의 숫자 중 10개를 랜덤으로 출력
g=tf.get_default_graph()
print([op.name for op in g.get_operations()])
# 실행 과정
sess=tf.Session()
print(sess.run(x2))
sess.close()
Tensorflow 실행 구조
Tensorflow Session은 fetch와 feed 2가지 방법으로 처리 할 수 있습니다.
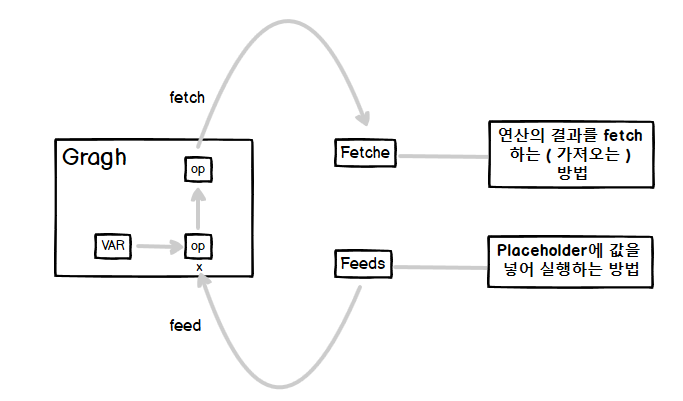
fetch는 Tensor에 할당 되어야 실제 Session에서 실행을 할 수 있습니다.
- 한개 실행할 때
import tensorflow as tf
a=tf.constant(1)
b=tf.constant(2)
c=tf.add(a,b)
sess=tf.Session()
print(sess.run(c))
sess.close()
# 또는
import tensorflow as tf
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(tf.add(1,2).eval())
- 여러 개 실행할 때
import tensorflow as tf
input1=tf.constant(3.0)
input2=tf.constant(2.0)
input3=tf.constant(5.0)
# fetch 여러 개 되는 부분
intermed=tf.add(input2,input3)
mul=tf.multiply(input1,input3)
with tf.Session() as sess:
result=sess.run([mul,intermed])
print(result)
feed 같은 경우는 Session에서 반드시 feed_dict로 처리 값을 할당해주어야 합니다.
import tensorflow as tf
a=tf.placeholder("float")
b=tf.placeholder("float")
y=tf.multiply(a,b)
z=tf.add(y,y)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
print(sess.run(y,feed_dict={a:3, b:3}))
print(sess.run(z,feed_dict={a:4, b:4}))
그래서 응용하여 구구단을 출력해보자면 아래와 같이 작성 할 수 있습니다.
import tensorflow as tf
## 구조(그래프) 선언부
x = tf.Variable(0, name='x')
# tensorboard 로 그래프를 그리기 위해서는 name 을 지정해 줘야한다.
y = tf.Variable(0, name='y')
# name 을 지정할 때 이름이 중복되면 안되고, 중복 사용을 위해서는
z = tf.multiply(x, y, name='z')
# 다른 옵션을 사용해야 한다.
model = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 변수(노드)를 위치 및 생성
merged = tf.summary.merge_all() # 그래프를 그리는데 사용될 변수(노드)를 취합
## 선언한 구조(그래프) 실행부
with tf.Session() as sess: # 세션(하나의 사용자) 생성
sess.run(model) # 위에서 생성한 그래프 구조를 실행
for i in range(2, 10):
for j in range(1, 10):
print(i, ' x ', j, ' = ',sess.run(z,feed_dict={x:i, y:j}))
# 초기화된 변수에 값을 feed
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('./logs', sess.graph)
# tensorboard 그래프를 그리는데 사용할 실행 로그를 저장할 폴더 지정
